Linux
cat command in Unix/Linux with 10+ examples [2025]
Let’s Learn cat command in Unix/Linux with Practical Examples :
The cat command in Unix/Linux is one of the most commonly used Linux commands on a day-to-day basis whether by novices or experienced Linux users. cat is short for concatenating and is mainly used for creating either single or several files at an instance, or viewing the contents of a file. In this article, we dive deeper and explore the cat command in Unix/Linux with example usages.
Cat command in Linux with examples
The most basic syntax for using cat command is as shown below
|
1 |
$ cat [options] file_name |
Let’s now take a closer look at the options that are mostly used with the cat command.
1. To view file content using cat command
To have a peek at a file without any options, simply use the syntax
|
1 |
$ cat filename |
For instance, to check the contents of a file /etc/hosts/code> run the command:
|
1 |
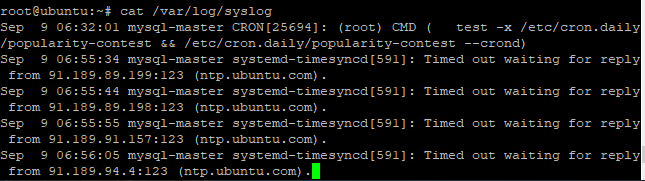
$ cat /var/log/syslog |
Sample output
2. View Mutiple files in a single command
To view multiple files at a go with cat command, use the syntax:
|
1 |
$ cat file1 file2 |
For example
|
1 |
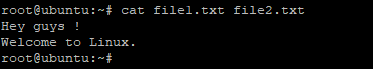
$ cat file1.txt file2.txt |
Sample output
3. Display line numbers using the -n option
To make your display neater, and more presentable, you may want to number the lines of your output. To achieve this, use the -n option as shown below
|
1 |
$ cat -n file_name |
For instance
|
1 |
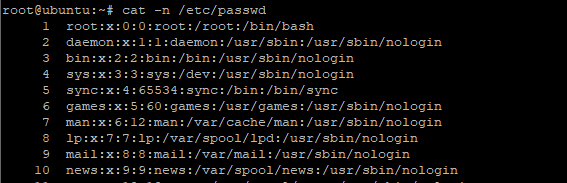
$ cat -n /etc/passwd |
Sample output
4. Create a file using the cat command
To create a file using cat command use the syntax
|
1 |
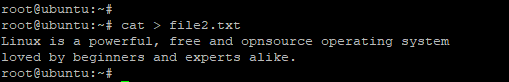
$ cat > filename |
Next, type the contents of the file and finally hit CTRL +D to save the file
5. Copy contents of one file onto another
With cat command, you can easily copy file contents of one file into another using the standard redirection operator > as shown below.
|
1 |
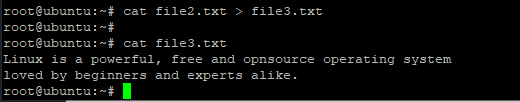
$ cat file2.txt > file3.txt |
If the file being copied to does not exist, it will be created automatically.
NOTE
Extra caution should be taken while using the standard redirection operator because it overwrites the contents of an existing file.
6. Redirect several files into one file
Similarly, you can redirect content from multiple files into one file using the syntax:
|
1 |
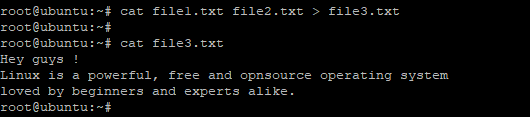
$ cat file1.txt file2.txt > file3.txt |
Sample output
7. Appending text to a file
if you want to append text and not overwrite the existing content, use the double greater sign symbol (>>). The content of one file will be added or appended at the end of the next text file.
|
1 |
$ cat file2.txt >> file3.txt |
8. Redirect standard input using redirection operator
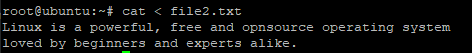
you can use the redirection operator less than (<) to read contents from a file. The syntax for this is:
$ cat < file2.txt
Sample output
9. Display the ‘$’ sign at the end of every line
If you wish to display the $ at the end of every line, use the -e option as shown below:
|
1 |
$ cat -e file3.txt |
Sample output
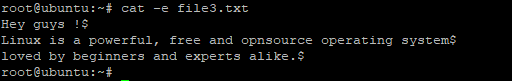
From the output above, you can see that there a dollar sign ($) at the end of every file.
10. Display all files of a certain type
To display the content of all files of a certain file type, for example, text files use the wildcard symbol as seen in the command below
|
1 |
$ cat *.txt |
Sample output
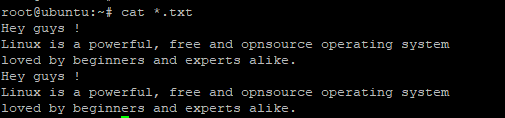
As you can see from the output above, the command displays all content from all the text files with a .txt file extension.
Take away
In this article, we demonstrated the usage of cat command alongside some helpful examples and tips. The cat command is usually helpful in creating and viewing text files as well as appending content at the end of a file. We do hope that this tutorial was helpful. Fee free to try out some of the commands.
-

 DevOps6 years ago
DevOps6 years agoSaltstack Tutorial for beginners [2025]
-

 DevOps6 years ago
DevOps6 years agoHow to build a Docker cron job Container easily [2025]
-

 Linux6 years ago
Linux6 years agomail Command in Linux/Unix with 10+ Examples [2025]
-

 DevOps6 years ago
DevOps6 years agoDocker ADD vs COPY vs VOLUME – [2025]
-
 DevOps5 years ago
DevOps5 years agoHow to setup Pritunl VPN on AWS to Access Servers
-

 Linux6 years ago
Linux6 years agoGrep Command In Unix/Linux with 25+ Examples [2025]
-
Linux5 years ago
How To setup Django with Postgres, Nginx, and Gunicorn on Ubuntu 20.04
-

 Linux6 years ago
Linux6 years agoFind command in Unix/Linux with 30+ Examples [2025]

