Linux
Whereis command in Linux with 10+ Examples [2023]
Let’s Learn whereis command in Linux with Simple Examples :
While working away on the command-line, one might need to find out the location of a command or binary file. The find command can be used for this task, but it is painfully slow and ends up taking much of your time and may also provide undesired results. The whereis command in Linux is ideal for quickly finding the location of a binary or source file in a system.
Whereis command in Linux is preferred due to its speed and accuracy in finding out the location of a command or binary files. More importantly, running the whereis command doesn’t require you to have root privileges. Let’s dive in and take a look at the whereis command usage with examples.
Whereis command usage in Linux
The basic syntax of the whereis command is:
1) Find the location of a command
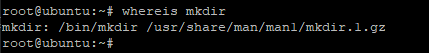
To find out the location and man pages of a Linux command for instance,mkdir run the command
Sample output
2) Search for specific files/manuals
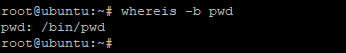
If you wish narrow down your search specifically to the binary file, use the -b option as shown in the command below.
Sample output
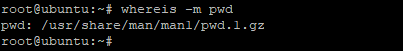
To search for man pages only use the -m option as shown.
Sample output
3) View paths that whereis uses for searching
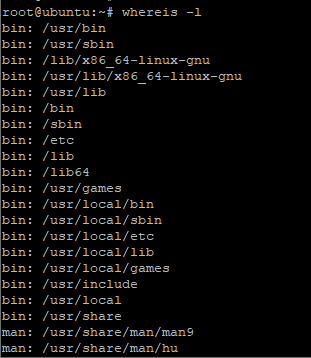
To take a quick peek at the directories that whereis command traverses while searching for command , files and man pages, use the -l option.
Sample output
4) Limit the search depth for whereis command
Usually, whereis command searches for commands and files in well-defined, hard-coded paths. However, you can limit the search depth using the -B option. For instance, to limit whereis to search binary files up to /bin, use the -B option as shown:
the -f option terminates the directory list whilst signaling the beginning of file names.
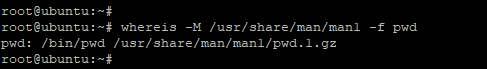
To limit the search directory for man pages, use the -M option as shown
Sample output
5) Check whereis version
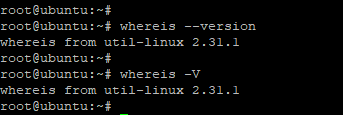
if you wish to check the version of whereis command, use the -V option or –version flag as shown.
OR
Sample output
6) Display whereis help options
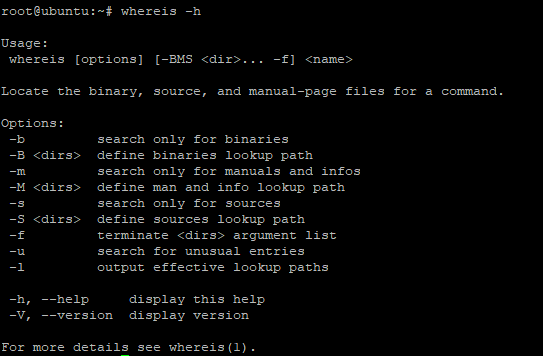
To view the help page section that gives more insight on the options that can be used by whereis command, use the -h option or –help flag.
OR
Sample output
And with that, we come to the end of our tutorial. We welcome you to try out the commands and get back to us with your findings.
-

 DevOps55 years ago
DevOps55 years agoSaltstack Tutorial for beginners [2023]
-

 DevOps55 years ago
DevOps55 years agoHow to build a Docker cron job Container easily [2023]
-

 Linux55 years ago
Linux55 years agomail Command in Linux/Unix with 10+ Examples [2023]
-

 DevOps55 years ago
DevOps55 years agoDocker ADD vs COPY vs VOLUME – [2023]
-
 DevOps55 years ago
DevOps55 years agoHow to setup Pritunl VPN on AWS to Access Servers
-

 Linux55 years ago
Linux55 years agoGrep Command In Unix/Linux with 25+ Examples [2023]
-
Linux55 years ago
How To setup Django with Postgres, Nginx, and Gunicorn on Ubuntu 20.04
-

 Linux55 years ago
Linux55 years agoFind command in Unix/Linux with 30+ Examples [2023]

